Fat talks and the body listens
The relationship between glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity and obesity
The Relationship between Glucose Metobolism, Insulin Sensitivity & Obesity
Obesity is a triggering factor for diabetes associated with insulin resistance. In individuals who are obese, higher amounts of non-esterified fatty acids, glycerol, hormones, and pro-inflammatory cytokines that could participate in the development of insulin resistance are released by adipose tissue.
Obesity-associated insulin resistance
Obesity leads to ectopic fat storage and an increase in FA metabolites that inhibit insulin signaling through activation of PKC in liver and muscle.
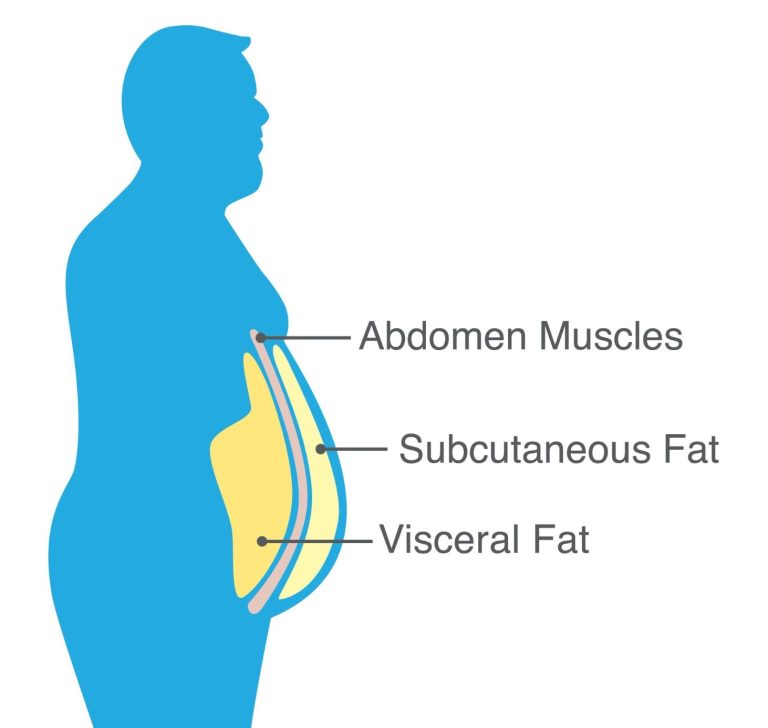
Visceral & Subcutaneous Fats
Visceral fat makes chemicals and hormones that can be toxic to the body. Visceral fat produces more of these toxic substances than subcutaneous fat, so it can be more harmful to your health. Because of this, visceral fat carries a range of health risks for everyone.
Palmitoleic Acid in Provinal®
Mechanism• Palmitoleic acid (POA) levels increase during obesity. It counters glucotoxicity and elevated saturated fat burden. During obesity POA rescues the obesity associated lipotoxicity.
"These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease;"
© Copyright. All rights reserved.
We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details and accept the service to view the translations.